IVF Journey Timeline Visualizer
This interactive timeline shows the 5 main stages of IVF treatment with estimated durations and key actions. Click on any stage to learn more details.
Ovarian Stimulation
8–14 days
Final Egg Maturation
1 day (trigger)
Egg Retrieval
0.5 days
Fertilization & Culture
3–5 days
Embryo Transfer
0–2 weeks
Quick Facts About IVF Duration
- A full fresh IVF cycle typically takes 4–6 weeks
- Frozen embryo cycles are usually shorter (no stimulation phase)
- Each stage has its own unique challenges and considerations
- Success rates vary significantly by patient age and medical history
When couples start the journey toward parenthood, In vitro fertilization is a medically assisted reproductive technique that joins an egg and sperm outside the body, then places the resulting embryo back into the uterus. Knowing the IVF stages helps you prepare emotionally and logistically, so you’re not caught off guard by each appointment, medication, or test.
Stage1 - Ovarian Stimulation (Ovulation Induction)
During the first two weeks, the goal is to coax the ovaries into producing multiple mature eggs instead of the single egg released naturally each month.
- Gonadotropins (usually a mix of FSH and LH) are injected daily. These hormones mimic the body’s natural signals.
- Doctors monitor growth with ultrasound scanning and blood tests for estradiol levels.
- Typical stimulation lasts 8-14 days, but the exact timeline depends on age, ovarian reserve, and medication dose.
Common concerns in this phase include injection site pain, bloating, and mood swings. Staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and keeping a simple injection log can ease the stress.
Stage2 - Final Egg Maturation (Trigger)
Once follicles reach the desired size (usually 18-20mm), a "trigger" shot is administered to complete the egg’s final maturation.
- The trigger is typically human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) or a GnRH agonist.
- Timing is critical: the egg retrieval is scheduled 34-36hours after the trigger, before ovulation occurs naturally.
- Patients are advised to avoid heavy exercise and to arrange transportation, as the trigger can cause mild cramping.
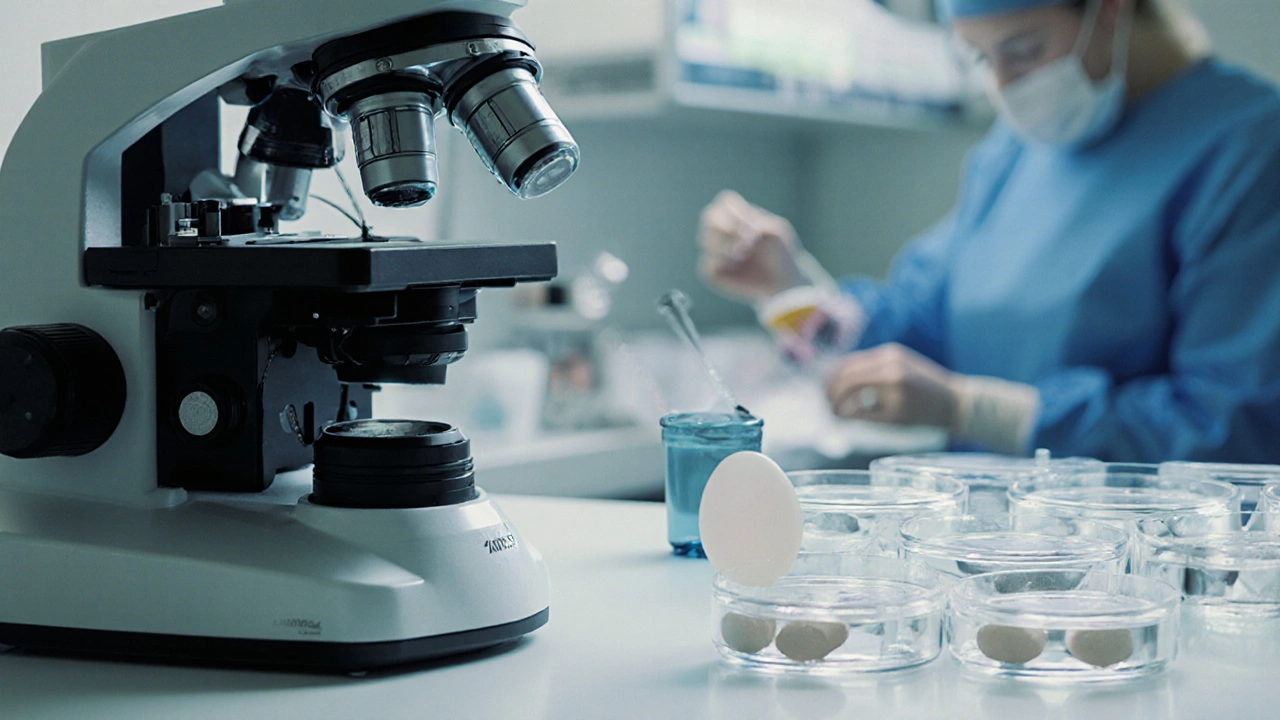
Stage3 - Egg Retrieval (Aspiration)
Under light sedation, a thin needle guided by transvaginal ultrasound punctures each follicle to collect the eggs.
- The procedure lasts 15-30minutes, and most women experience only mild discomfort afterward.
- Collected eggs are immediately handed to the embryology lab, where they are assessed for maturity.
- In the same session, sperm-either from a partner or a donor-are prepared for fertilization.
Potential side effects include spotting or a brief feeling of fullness. Recovery tips: wear loose clothing, use a cold pack on the lower abdomen, and avoid sexual activity for 24-48hours.
Stage4 - Fertilization & Embryo Culture
There are two main ways to join the egg and sperm:
- Conventional IVF - sperm and egg are placed together in a culture dish and left to fertilize naturally.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) - a single sperm is injected directly into the egg, boosting fertilization chances for male‑factor issues.
After fertilization, embryos are cultured for 3-5days. During this window, labs may perform pre‑implantation genetic testing (PGT) to screen for chromosomal abnormalities, especially for older patients or recurrent miscarriage cases.
- Embryos reaching the blastocyst stage (around day5) have a higher implantation potential.
- Good-quality embryos are either transferred fresh or frozen for future use (cryopreservation).
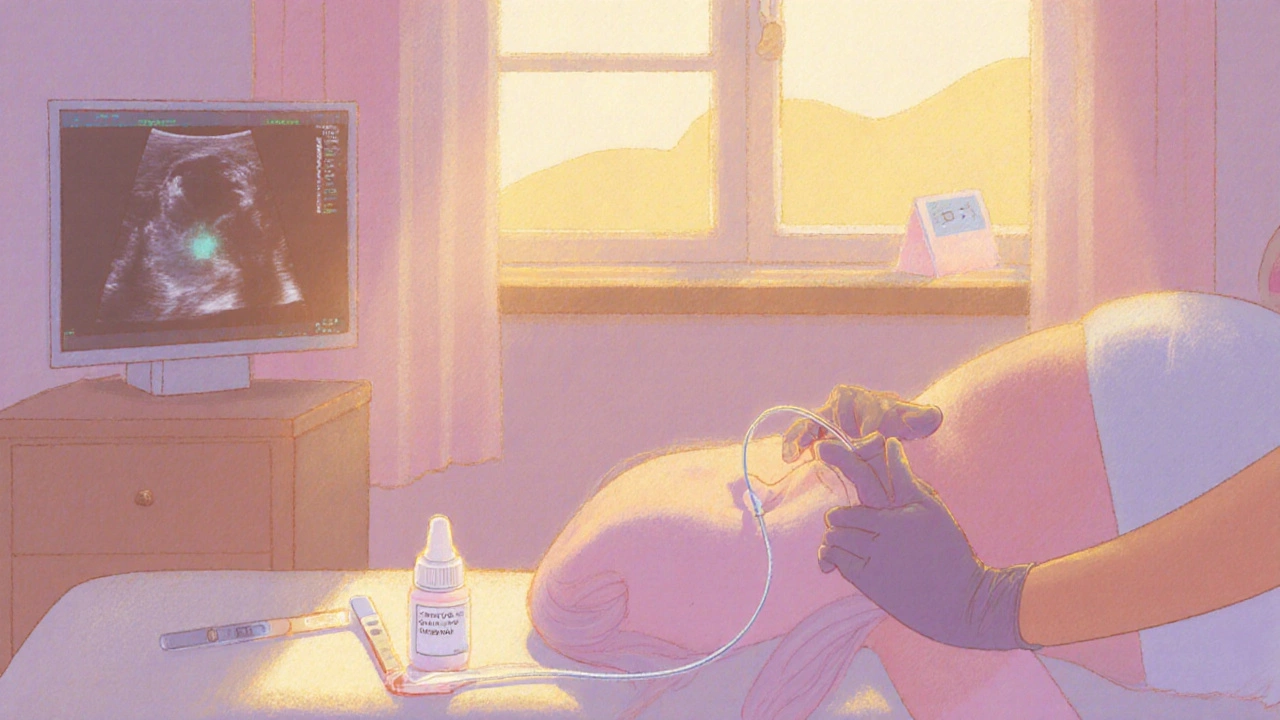
Stage5 - Embryo Transfer & Luteal Support
Whether a fresh or frozen embryo, the transfer involves a thin catheter placed through the cervix into the uterus.
- The procedure is painless; many clinics use ultrasound guidance to ensure optimal placement.
- After transfer, patients receive luteal phase support-usually progesterone shots, vaginal gels, or oral tablets-to sustain the uterine lining.
- Two weeks later, a blood test for beta‑hCG determines if implantation succeeded.
If the test is positive, follow‑up scans confirm a viable pregnancy. If not, doctors discuss the next steps, which might include another frozen embryo transfer or adjusting the stimulation protocol.
Quick Reference Table
| Stage | Duration (days) | Main Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Ovarian Stimulation | 8-14 | Hormone injections, ultrasound & hormone monitoring |
| Trigger | 1 (34-36h before retrieval) | hCG or GnRH‑agonist injection |
| Egg Retrieval | 0.5 (procedure day) | Transvaginal ultrasound‑guided aspiration under sedation |
| Fertilization & Culture | 3-5 | IVF or ICSI, embryo growth, optional PGT |
| Embryo Transfer & Luteal Support | 0-2 (transfer day + 14‑day pregnancy test) | Catheter placement, progesterone support, hCG test |
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a complete IVF cycle take?
From the first hormone injection to the pregnancy test, a typical fresh IVF cycle spans 4-6weeks. Frozen‑embryo cycles are slightly shorter because the stimulation phase is omitted.
Can I work or travel during the stimulation phase?
Most patients continue regular work with minimal disruption. Travel is possible but should avoid high‑altitude flights after the trigger shot, as it may affect implantation.
What are the success rates for each stage?
Success hinges on embryo quality and uterine receptivity. In 2024 Indian data, the overall live‑birth rate per fresh transfer was ~38% for women under 35, dropping to ~15% after 40. Cryopreserved transfers tend to have slightly higher rates due to better embryo selection.
Is it normal to feel emotional during the IVF journey?
Absolutely. Hormonal fluctuations, the high stakes, and waiting periods trigger anxiety for many couples. Counseling, support groups, and mindfulness apps have shown measurable benefits.
What happens if the fresh transfer fails?
Frozen embryos can be thawed for a later transfer, often with a different protocol. Doctors may also adjust medication doses, recommend additional PGT, or explore alternative options like donor eggs.
